An introduction to Cyclic Yoga®
Cyclic Yoga is the art of sequencing yoga asana, pranayama and mudra techniques to maximize their benefits and energize the mind and body. This style of yoga was developed by Indian yogini, Maya Machawe, in collaboration with Iranian psychologist Saed Ahmadi. It is based on the belief that practicing a well-balanced sequence or series of asanas enhances the health benefits and therapeutic effects of each pose, making the practitioner feel more relaxed and refreshed after each session.
Each cycle is composed of a certain number of asanas and their associated actions, designed to be performed in a specific sequence in relationship with each other. The sequencing of asanas in a cycle involves an increasing level of complexity, moving from simple to complex poses. as well as maintaining body ease, balance and stability for consecutive asanas. Therefore, practicing a complete cycle utilizes the properties of each asana to pave the way for moving on through the next pose easily and more comfortably.
Cyclic Yoga practitioners will experience more significant psychological and physical well-being. They frequently report profound relaxation, increased flexibility and a lightsome feeling after a Cyclic Yoga session.
A novice Cyclic Yoga student needs to learn the fundamentals of alignment with each individual asana in a desired manner. For this purpose, the founders of the Cyclic Yoga style have designed four separate skills and established four distinct levels of preparedness for practice, namely: Primary, Intermediate, Advanced and Cycles.
- The Primary Level: The initial phase is to learn how to go through the correct form of each asana as well as get familiar with the benefits and limitations of these poses. This level of training course encompasses learning a few simple movements to prepare the body for going through the key yoga asanas. At this level, the body will get rid of its tensions, while joints and tendons will gain the required flexibility to move onto the next levels. The muscles of the abdomen, legs and back will gradually become powerful enough to perform more rigorous yoga poses.
- The Intermediate Level: The second step is to learn how to create correct contraction and stretching in a target muscle group and also get familiar with the forces imposed on the body in each yoga pose. While concentrating on muscular contraction and stretching, students will come to understand the key points of moving the body through each asana during the second level.
- The Advanced Level: The third phase is dedicated to increasing the duration of each asana as well as improving the general flexibility of the body. At this level of training the Cyclic Yoga student acquires ancient as well as scientific knowledge about yoga asanas. When the student is able to hold each asana for more than 30 seconds using correct alignment and the proper stretching and contracting techniques, he or she is ready to commence practicing the advanced cycles.
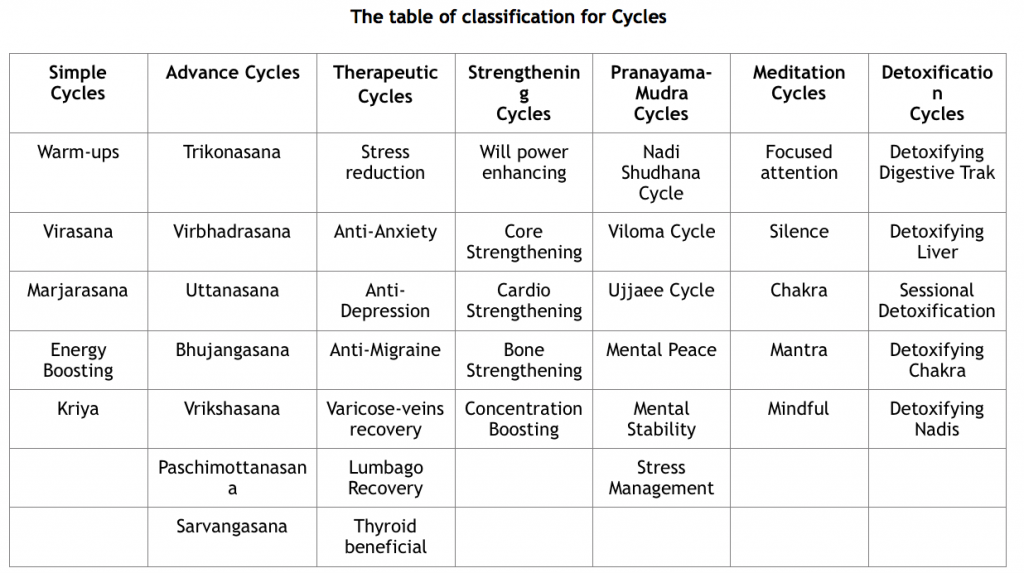
- The Cyclic Level: The main cycles can be classified into six categories: Simple, Advanced, Therapeutic, Strengthening, Pranayama-Mudra, Meditation and Detoxification.
- Simple Cycles: Simple cycles can be easily performed by everyone, even students at the primary level of yoga or individuals experiencing physical limitations.
- Advanced Cycles: Advanced cycles, consisting of rigorous and powerful yoga asanas, require special tutorials and sufficient flexibility in order to be performed.
- Therapeutic Cycles: These cycles are designed to assist therapeutic aspects and a person may execute them according to his or her physical capabilities and aptitudes.
- Strengthening Cycles: All strengthening cycles have a goal to tackle. These cycles are designed to increase individual resilience and build physical and psychological strength.
- Pranayama-Mudra Cycles: Pranayama Cycles are designed to harmonize the flow of prana, running through the psychic channels (nadis), and aid in balancing the frequency of chakras.
- Meditation Cycles: Meditation cycles cultivate awareness and promote mental peace and tranquility.
- Detoxification Cycles: These are Ayurveda based cycles, specially designed to balance doshas, reduce ama and strengthen kosha.
Method of practicing the cycles
Before implementation of any Cycle, sit in a relaxed position. Close your eyes. Breathe calmly and slowly. Relax the entire body and mind to obtain mental peace and body awareness. Calmness of body and mind can enhance strength and also deepen physical moves.
Simple or Advanced Cycle: The simple and advance Cycles are practiced in three stages:
- Stage one: Warm up phase
The goal of this phase is to awaken muscles and get the blood pumped all over body. Warming up reduces risk of injury. At this stage you either can use Surya Namaskar Cycles or can perform the pre-designed Cycles of warm up asanas or can execute the same sequence of asanas included in aimed Cycle using minimum amount of effort and pauses. Warm up phase increases heart rate and awareness of body movements.
- Stage two: Experience the feeling of Asanas
During the second stage poses from targeted Cycles are implemented according to suggested consequence with full awareness, using all alignment techniques. Each asana should be performed according to individual physical capabilities and aptitudes.Duration of holding asanas must be according to strength of the body. While each individual asana in a Cycle may demand separate holding time, generally to gain best results, asana from each Cycle should be hold for 30 seconds starting initially from 10 seconds and increasing gradually over a period of time to 30 seconds.
It is always best to count the number of breaths because it keeps you engaged and focused. In this way the chain of poses will be harmonized with the breathing rhythm. This stage of Cyclic Yoga is aimed at cardio advantages.
- Stage three: Integrate body and mind
The final aim of Cycles is to release tension and integrate the effects of asanas to create energetic balance between the body and mind. This can be done either by practicing Savasana Cycle or executing suggested breathing Cycles.
Therapeutic Cycles: These cycles are designed as a package including special asana, pranayama and mudra techniques to relieve discomfort caused by certain disease and aids in rehabilitation. A person can execute the sequence of therapeutic cycles according to individual physical aptitude. Each cycle is repeated once or maximum twice depending upon personal choice. To get incredible results, it is important to follow the implementation tactics (with or without using supports like wall, chairs, blocks, stretch straps etc.) and also following suggested rounds of Pranayama and or Mudra techniques specified in these cycles.
Strengthening Cycles: Strengthening Cycles introduce mental or physical strength workout routine. These cycles are implemented for certain days or weeks and after passing through a resting period for a week or more could be repeated again. These cycles also apply asana, pranayama, mudra practices and/or even sometimes includes guidelines for nutrition as well as codes of behavior from ethics of yoga (yama & niyama).
Pranayama-Mudra Cycles: These cycles are implemented in two phases.
- Mudra phase: Duration of holding each mudra lasts for desirable period of personal choice, unless, otherwise suggested to synchronize it with specific breathing pattern and focusing pattern.
- Pranayama phase: Types of breathing exercises of distinct pranayama applicable in the cycle must be repeated for given numbers of rounds and sets.
Meditation Cycles: To get maximum results, Meditation cycles are programmed to execute for certain duration of days. In each cycle a special schedule of practice is suggested to be carried on. This schedule contains implementation of special bodily exercises, breathing techniques and a specific style of meditation.
Cleansing Cycles: These cycles vary in implementation depending upon type, kind and target of detoxification. These cycles are based on the fundamentals of Ayurveda.

